|
|||||||||
| PREV PACKAGE NEXT PACKAGE | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
See:
Description
| Interface Summary | |
| CollectionOperator | CollectionOperator is the toplevel interface for collection operators. To be able to prove the correctness of a subclass, a model method is provided which acts like an abstract precondition for methods that operate on the elements of collections. Collection operators are typically used as anonymous inner classes, in which case some assertions are known to be true for the collection. |
| Dispenser | A Dispenser is a Collection with an inherent order of removal of its objects, e.g. |
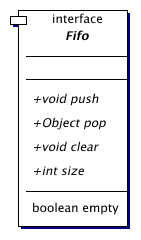
| Fifo | Interface for first-in first-out like datastructures.

|
| MapOperator | MapOperator is the toplevel interface for map operators. To be able to prove the correctness of a subclass, a model method is provided which acts like an abstract precondition for methods that operate on the object-key pair of maps. Map operators are typically used as anonymous inner classes, in which case some assertions are known to be true for the pairs in the map. |
| PriorityQueue | A PriorityQueue is a container of objects with an associated priority/ordering, that allows the retrieval of the element with the smallest value. |
| Class Summary | |
| AbstractDispenser | AbstractDispenser provides an implementation for the add method that always returns true and delegates to an abstract method for the actual adding. |
| AbstractFifo | AbstractFifo provides an implementation for several Dispenser methods, delegating them to the corresponding Fifo methods. |
| AbstractPriorityQueue | AbstractPriorityQueue provides an implementation for getNext and removeNext. |
| Accumulator | A class of objects that accumulate over a collection.
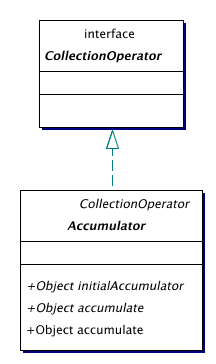 The Accumulator class is the general class for visiting a collection
while passing some object to the next element.
The Accumulator class is the general class for visiting a collection
while passing some object to the next element. |
| AndFilter | The effect of this filter is the same as of a filter with the
conjunction of the criteria of the filters it was build with.
 Different filters can be applied to a collection consecutively.
Different filters can be applied to a collection consecutively. |
| ArrayCursor | A class of objects that point to a certain index in a multi-dimensional array. |
| Arrays | A class with static methods for arrays |
| BasicBinomialHeap | A BasicBinomialHeap is a Heap that consists of a forest of Binomial Trees. Most operations are O(log(n)). |
| BasicBinomialHeap.BinomialTree | |
| BinomialHeap | A BinomialHeap is a Heap with most of its operations O(1) or O(log(1)). |
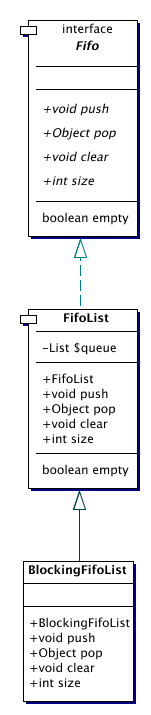
| BlockingFifoList | Synchronized fifo list that will block the request to pop the first object
until a first object is present.
|
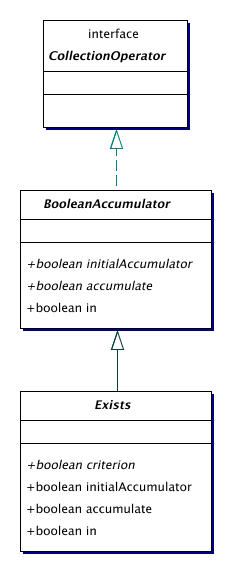
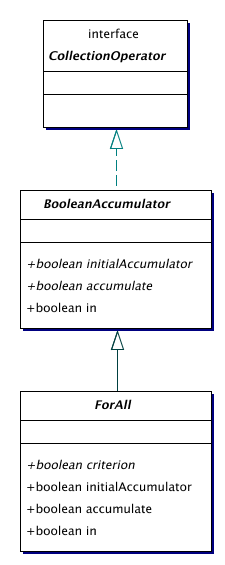
| BooleanAccumulator | A boolean accumulator for collections. |
| Collections | A utility class for perform operations on collections similar to java.util.Collections. |
| ComparableComparator | Deprecated. |
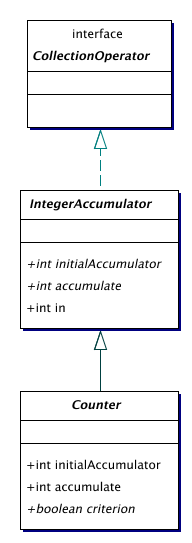
| Counter | An IntegerAccumulator that counts the number of items in a collection that
satisfies some criterion.
 A convenience accumulator of collections that checks
elements of a collection satisfy the criterion defined in
A convenience accumulator of collections that checks
elements of a collection satisfy the criterion defined in
public boolean criterion(Object element).
As with the accumulator, this class can best be used as an anonymous
inner class, as shown below.
int number = new Counter() {
public boolean criterion(Object element) {
// criterion code
}
}.in(collection);
|
| Exists | A boolean exists operator.
 A convenience accumulator of collections that checks whether some
element of a collection satisfies the criterion defined in the abstract
method
A convenience accumulator of collections that checks whether some
element of a collection satisfies the criterion defined in the abstract
method public boolean criterion(Object element).
As with Accumulator, this class can best be used as an anonymous
inner class.
boolean bool =
new Exists() {
/oo
o also public behavior
o
o post (* additional precondition for criterion method *)
o
o public model boolean isValidElement(Object element);
o/
/oo
o also public behavior
o
o post \result == ((MyType)element.someProperty() ...)
o/
public boolean criterion(Object element) {
// criterion code
}
}.in(collection);
|
| ExtendedComparator | Deprecated. |
| FifoList | FifoList is a class of objects that represent simple first-in first-out lists . |
| Filter | A filter for collections. |
| ForAll | A boolean for-all operator.
 A convenience accumulator of collections that checks whether all
elements of a collection satisfy the criterion defined in the abstract
method
A convenience accumulator of collections that checks whether all
elements of a collection satisfy the criterion defined in the abstract
method public boolean criterion(Object element).
As with Accumulator, this class can best be used as an anonymous
inner class.
boolean bool =
new ForAll() {
/oo
o also public behavior
o
o post (* additional precondition for criterion method *)
o
o public model boolean isValidElement(Object element);
o/
/oo
o also public behavior
o
o post \result == ((MyType)element.someProperty() ...)
o/
public boolean criterion(Object element) {
// criterion code
}
}.in(collection);
|
| IntegerAccumulator | An integer accumulator for collections. |
| InverseComparator | Deprecated. |
| Mapping | A mapping of collections.
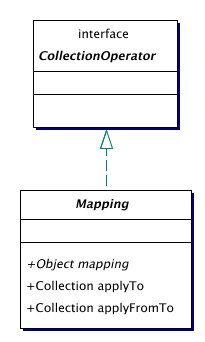 Mappings exchange an element for another element,
calculated based on the original element.
Mappings exchange an element for another element,
calculated based on the original element. |
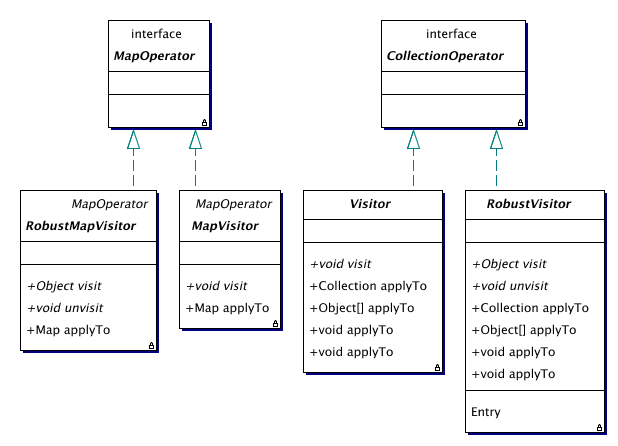
| MapVisitor | A visitor of maps. |
| ObjectArrayIterator | A class of iterators for multi-dimensional arrays of objects. |
| RobustMapVisitor | A robust visitor of maps. |
| RobustVisitor | A robust visitor of collections. |
| Singleton | |
| SkipList | A collection which is actually a sorted list.
A skiplist is a sorted list with an average O(log(n))
behavior for
add() and
remove() |
| SkipListPQ | A SkipList based priority queue |
| Stack | A Stack is a Dispenser whose elements can be removed in last-in first-out order. |
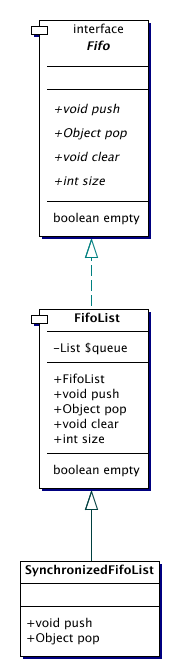
| SynchronizedFifoList | Synchronized version of a FifoList.
|
| TransitiveClosure | An operator that calculates the transitive closure of a graph of objects.
 Objects of this class calculate the transitive closure of a graph,
defined by
Objects of this class calculate the transitive closure of a graph,
defined by public Set getConnectedNodes(Object node),
starting from a set of nodes or a single start node. |
| TypeFilter | A class of filters that use the type of an object as criterion.
 This filter uses the type of elements of the filtered collection as criterium.
This filter uses the type of elements of the filtered collection as criterium. |
| Visitor | A class of collection operators that can perform a certain action on all
element of a collection.
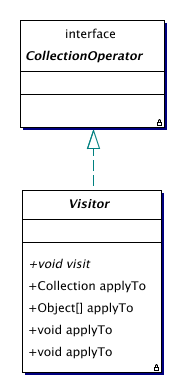 Visitor
The Visitor class is a
replacement for the
Visitor
The Visitor class is a
replacement for the java.util.Iterator class that allows a
programmer to perform a certain action on all elements of a collection. |
| Exception Summary | |
| ZeroDimensionException | A class of exceptions indicating the attempt to use a class in this package with an object array that has at least one dimension equal to zero. |
Provides for operations on collections. These operations can be seen as software theorems. Instead of writing the same error-prone iterations over and over again, the classes of this package can be used. Using these classes will make iterations much easier to read and a lot easier to prove.
A manual for each of the classes follows below.
CollectionOperator is the toplevel interface for operations on collections. It only contains a model method (a specification-only method) isValidElement(Object element). This method is needed in order to prove the correctness of subclasses.
Set operations are the one and only reason for the creation an the success of for example SQL. You can perform very complex operations with a very easy syntax. In traditional object-oriented programs, they are still the most complex constructions because they require loops to be written, which are difficult to write (how many times did you write a loop correct from the first time ?). Another drawback is that these loops, for example to check whether all elements of a collection satisfy some criterion, have to be written over and over again because they are always implemented with low-level constructions (for, while) which are not reusable.
With the classes in this package, the same functionality can be added to object-oriented programs. Using internal iterators, they provide set operations which can easily be adapted to perform specific things by subclassing them. The documentation of the classes explains how to do that.
As a result of the use of internal iterators, complex nested iterations can be replaced by a declarative implementation that is both very easy to read and write.
Visitors are object that can perform a certain action on all element of an object structure.
The Visitor class is a replacement for the java.util.Iterator class that allows a programmer to perform a certain action on all elements of a collection.
The MapVisitor class is similar to the Visitor class, but it operates on maps instead of collections. The only difference between the two classes is an additional argument in the visit method.
Of course, sometimes exceptions can be thrown during a visit. The default behaviour when an exception occurs, is to undo all changes that were made and throw an exception to the caller of the method. This means that the actions that were performed on elements visited before the element that caused the exception, have to be undone. The RobustVisitor class adds support for handling exceptions to the Visitor class.
As with the normal visitor, an additional class RobustMapVisitor is made for visiting maps when exceptions can occur.
An accumulator acts like a visitor, but passes an argument from each visit to the next. Because we cannot write code that works for both Object types and primitive types, we have separate accumulators for Object, and each primitive type (currently only int and boolean). Wrapping primitive values in their wrapper class is annoying to work with, and causes an unnecessary performance penalty.
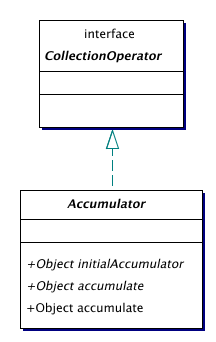
The base class of objects that use an Object as accumulator.
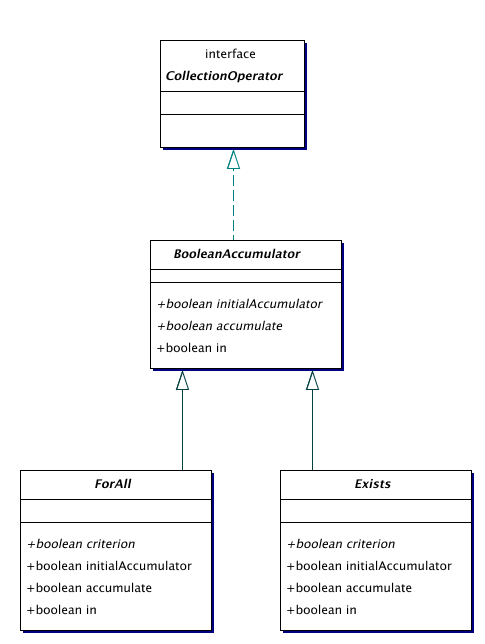
The BooleanAccumulator class is almost identical to Accumulator. The return types have been changed to boolean, and the accumulate has been renamed to in.
The boolean accumulator ForAll checks whether some boolean criterion is satisfied by all elements in a collection.
The boolean accumulator Exists checks whether some boolean criterion is satisfied by at least one element in a collection.
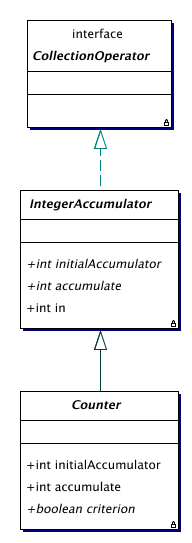
A Counter is an integer accumulator that counts how many object in a given collection satisfy some criterion.
Filters are collection operators that filter certain objects out of a collection. Given a criterion, a filter can discard or retain the objects satisfying that criterion.
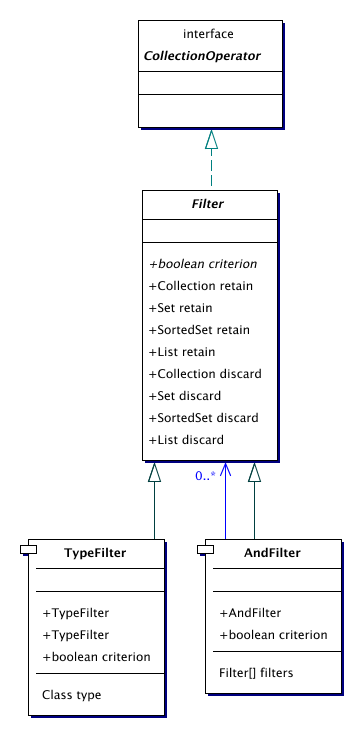
Filter is the top class of the filters that operate on collections. It implements the retain and discard methods. The criterion must be defined by subclasses.
TypeFilter is a special filter that uses the type of the object in the collection as criterion.
AndFilter is a special filter that acts like a filter with a criterion that is the "and" of the criteria of the filters it is composed of.
Fifo queues are first-in-first-out queues.
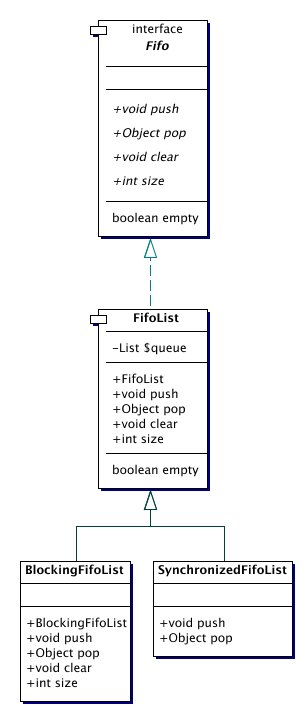
Fifo is the top interface of all Fifo queues.
FifoList is an implementation of the Fifo interface.
FifoList is a synchronized subclass of FifoList.
FifoList is a subclass of FifoList that is synchronized, and
blocks pop() requests when it is empty until an item is available.
|
|||||||||
| PREV PACKAGE NEXT PACKAGE | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||