|
|||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: INNER | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||
java.lang.Object
|
+--java.util.AbstractCollection
|
+--org.jutil.java.collections.SkipList
A collection which is actually a sorted list.
A skiplist is a sorted list with an average O(log(n))
behavior for
add() and
remove().
The worst case time complexity is O(n).
A skiplist looks like a linked list, but the difference is that the cells
of a skiplist have a number of forward pointers. The number of forward
pointers of a cell is called the level of that cell.
The level of a SkipList is
the maximum of the levels of its cells. The level of a SkipList can not
exceed its maximum level.
The i'th forward pointer of a cell points to the next cell of level
>= i, thus skipping a number of elements with level <i.
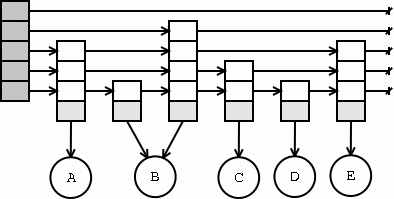
An example a skiplist is shown in the figure below.
The left cell is the header of the skiplist which contains
getMaxLevel() forward
pointers (but is not included in the level count for the list).
The crossed arrows point to the end of the list, indicating there is no
next cell of level i. The light grey field at the bottom of each cell is a
reference to the element that is represented by that cell. As you can see,
multiple cells can reference the same object because we are dealing with a
list.

The elements of a SkipList are sorted using a
Comparator,
which is given to the list at the time of construction.
The level of a cell is a random number between 1 and
getMaxLevel().
There is a fixed
probability
that a cell with a level >=i has a level >=i+1 (unless of course
i==getMaxLevel()).
It is the randomness that makes that a skiplist has an average
O(log(n))
add() and
remove()
because only a fixed number of cells must be changed to insert of remove a
cell (no structure has to be maintained).
With probability 0.25 the average number of forward pointers per element is 1.333. A maximum level L will be efficient for a SkipList containing about 4L elements. If you add much more elements than that, the number of cell with the maximum level will increase, so searching an element will take longer. The default level is 8.
For more information, go to ftp://ftp.cs.umd.edu/pub/skipLists.
| Field Summary | |
static java.lang.String |
CVS_REVISION
|
| Constructor Summary | |
SkipList(int maxLevel,
java.util.Comparator comparator,
float probability)
Initialize a new SkipList with the given maximum level, comparator and probability. |
|
SkipList(java.util.Comparator comparator)
Initialize a new SkipList with the given comparator. |
|
| Method Summary | |
boolean |
add(java.lang.Object object)
See superclass |
void |
clear()
See superclass |
boolean |
contains(java.lang.Object o)
See superclass |
java.util.Comparator |
getComparator()
Return the Comparator used to determine the order in which the elements are added to this SkipList. |
java.lang.Object |
getFirst()
Return the first object of this SkipList. |
int |
getMaxLevel()
Return the maximum level of this SkipList |
float |
getProbability()
Return the probability that a node of level >= i is a node of level >= i + 1 |
java.util.Iterator |
iterator()
See superclass |
boolean |
remove(java.lang.Object object)
See superclass |
boolean |
removeAll(java.lang.Object object)
See superclass |
void |
removeFirst()
Remove the first element of this SkipList. |
int |
size()
See superclass |
java.lang.String |
toString()
See superclass |
| Methods inherited from class java.util.AbstractCollection |
addAll, containsAll, isEmpty, removeAll, retainAll, toArray, toArray |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, wait, wait, wait |
| Methods inherited from interface java.util.Collection |
equals, hashCode |
| Field Detail |
public static final java.lang.String CVS_REVISION
| Constructor Detail |
public SkipList(java.util.Comparator comparator)
comparator - The Comparator used to determine the order of the elements
in this SkipList.
public SkipList(int maxLevel,
java.util.Comparator comparator,
float probability)
maxLevel - The maximum level of the nodes used internally by
this SkipList.comparator - The Comparator used to determine the order of the elements
in this SkipList.probability - The fraction of nodes of level >= i that has level >= i + 1| Method Detail |
public java.lang.String toString()
public int size()
public void clear()
public boolean contains(java.lang.Object o)
public java.lang.Object getFirst()
public int getMaxLevel()
public java.util.Comparator getComparator()
public float getProbability()
public java.util.Iterator iterator()
public boolean add(java.lang.Object object)
public void removeFirst()
public boolean remove(java.lang.Object object)
public boolean removeAll(java.lang.Object object)
|
|||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: INNER | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||