|
|||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: INNER | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||
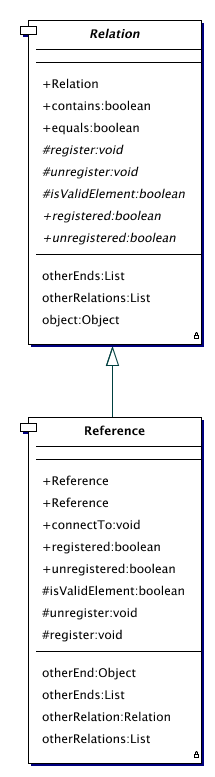
java.lang.Object
|
+--org.jutil.relation.Relation
|
+--org.jutil.relation.Reference
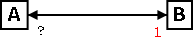
A class of Relation components for implementing a binding in which the object of the Reference has a relation with only 1 other object.

In UML this class is used for implementing multiplicity 1:
In Java, you get the following situation.
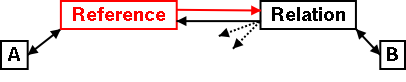
Note that the question mark is represented by a Relation object since
we don't know its multiplicity. The double binding between the Reference
object and A is made by passing this to the constructor of
Reference.
This is actually a lightweight version of the APElement class. of the Beedra framework of Jan Dockx.
This class is typically using in the following way.
public class B {
public B() {
_a = new Reference(this);
}
public A getA() {
return (A)_a.getOtherEnd();
}
public void setA(A a) {
_a.connectTo(a == null ? null : a.getBLink());
}
Reference getALink() {
return _a;
}
private Reference _a;
}
The other class must have a method getBLink(), which returns a
Relation object that represents the other side
of the bi-directional binding. In case the two classes are not in the same package that means
that getBLink() must be public there, but that is also the case when
not working with these components. Note that if the binding should not be mutable from class
B the setA() may be removed. Similarly, getALink() may
be removed if the binding is not mutable from class A.
| Class Specifications |
| public invariant getOtherRelation() != null ==> getOtherRelation().contains(this); |
| Field Summary | |
static java.lang.String |
CVS_REVISION
|
| Constructor Summary | |
Reference(java.lang.Object object)
Initialize a new Reference for the given object. |
|
Reference(java.lang.Object object,
Relation other)
Initialize a new Reference for the given object, connected to the given Relation. |
|
| Method Summary | |
void |
connectTo(Relation other)
Set the other side of this binding. |
java.lang.Object |
getOtherEnd()
Return the Object at the other end of this double binding. |
java.util.List |
getOtherEnds()
|
Relation |
getOtherRelation()
return the Relation this Reference belongs to |
java.util.List |
getOtherRelations()
See superclass. |
protected boolean |
isValidElement(Relation relation)
|
protected void |
register(Relation other)
See superclass |
boolean |
registered(java.util.List oldConnections,
Relation registered)
|
protected void |
unregister(Relation other)
See superclass |
boolean |
unregistered(java.util.List oldConnections,
Relation unregistered)
|
| Methods inherited from class org.jutil.relation.Relation |
contains, equals, getObject |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
clone, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait |
| Field Detail |
public static final java.lang.String CVS_REVISION
| Constructor Detail |
public Reference(java.lang.Object object)
object - The object at this side of the binding.
public Reference(java.lang.Object object,
Relation other)
object - The object at this side of the binding.other - The Relation component at the other side of the binding.| Method Detail |
public java.lang.Object getOtherEnd()
public java.util.List getOtherEnds()
public void connectTo(Relation other)
other - The new Relation this Reference will be connected to.
public boolean registered(java.util.List oldConnections,
Relation registered)
public boolean unregistered(java.util.List oldConnections,
Relation unregistered)
protected boolean isValidElement(Relation relation)
protected void unregister(Relation other)
protected void register(Relation other)
public Relation getOtherRelation()
public java.util.List getOtherRelations()
|
|||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: INNER | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||